 The model seeks to find the relevant variables that cause a country's economic growth (closed economy), as some help to improve the situation only in the short term and others that affect growth rates long term. All variables are taken that the model considers as significant in the growth process as exogenous, but shows the incidence of these in the growth process. The model uses the Cobb-Douglas:
The model seeks to find the relevant variables that cause a country's economic growth (closed economy), as some help to improve the situation only in the short term and others that affect growth rates long term. All variables are taken that the model considers as significant in the growth process as exogenous, but shows the incidence of these in the growth process. The model uses the Cobb-Douglas: 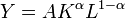
Defining variables, we have:
K = total capital
L = total labor force or labor used in production.
A = is a mathematical constant which depends on the level of technology.
And = Total [measured in monetary units, for example].
α = fraction of product from the capital or the income coefficient Diminishing marginal.
is known, moreover, necessarily, one can prove that α coincides with the full participation of capital in production (according to the analysis of total factor productivity). If alpha is α ~ 1, the production will be based on available capital and is almost independent of labor. There are reasons to believe that for many real situations the production function is Cobb-Douglas production function that is credible constant returns to scale and diminishing marginal returns to capital and labor. Later you will see that if one assumes that the production function is of this type, exit the possibility of convergence to a stationary product continues to grow by the rate of savings. Technically
the hypothesis that the production function is Cobb-Douglas function is not essential to the model, it would suffice to be a monotone increasing function of capital and the amount of work.
To formulate the model from the Cobb-Douglas function is defined for convenience:
• Product per capita cash and the amount of output per unit of labor and
• The capital stock per capita cash k as the amount of capital per unit labor
words, define the variables:
the hypothesis that the production function is Cobb-Douglas function is not essential to the model, it would suffice to be a monotone increasing function of capital and the amount of work.
To formulate the model from the Cobb-Douglas function is defined for convenience:
• Product per capita cash and the amount of output per unit of labor and
• The capital stock per capita cash k as the amount of capital per unit labor
words, define the variables:
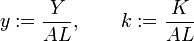
As we have assumed that the production function is Cobb-Douglas has the following relationship between yyk:

Assuming actual output per capita and the above function, we have that the smaller α will be a product per capita cash dwindling, ie the function takes the form of a root, although the function is divergent to infinity when k tends to infinity. The above function satsiface Inada conditions, namely:

These limits are known as Inada conditions, and explained that the derivative of, ie the marginal product of capital is 0 when k is high. It explains that when k is too low, the marginal product is very high. These latter conditions, although mathematically quite evident then imply that countries with low capital amount would grow at high rates, while countries with high amounts of capital grow at lower rates due to diminishing marginal returns this.
0 comments:
Post a Comment